While applying for a loan, lenders consider several factors to ensure that you’re a responsible borrower who can comfortably repay the debt. Lenders will only lend you money when they know you can pay them back, but how do they make sure? That’s where the debt-to-income ratio (DTI) comes in.
It’s a factor that lenders consider to assess your repayment capabilities, and having an understanding of it can be beneficial for your financial situation.
Read on to understand what Debt to Income Ratio is, its importance, and how to calculate it.
What is the Debt-to-Income (DTI) Ratio?
The Debt to Income (DTI) ratio is a financial metric that compares an individual’s monthly debt payments to their gross monthly income. Lenders commonly use it to assess a borrower’s ability to manage monthly payments and repay debts.
A lower DTI ratio indicates a healthier balance between debt and income, suggesting that the borrower is more likely to manage their debt payments effectively.
Conversely, a higher DTI ratio may indicate that the borrower has too much debt relative to their income and may have difficulty managing their obligations. Generally, lenders prefer a DTI ratio of 36% or lower.
Importance of Debt to Income Ratio
The Debt to Income (DTI) ratio is important for several reasons:
Lending Decisions
Lenders use the DTI ratio to evaluate a borrower’s ability to manage monthly payments and repay debts. It is an important factor in the approval process for mortgages, car loans, personal loans, and credit cards.
Interest Rates and Loan Terms
DTI is one of the important factors in deciding the loan terms. Borrowers with lower DTI ratios are usually offered better interest rates and more favorable loan terms because they are perceived as less likely to default on their loans. Conversely, a higher DTI ratio can lead to higher interest rates and less favorable loan terms due to the increased risk to the lender.
Financial Health Indicator
The DTI ratio is a good indicator of an individual’s financial health. It helps individuals understand their debt levels relative to their income and assess when they’re deep in debt.
Budgeting and Planning
By calculating and understanding their DTI ratio, individuals can create more realistic budgets and financial plans. This helps them recognize the portion of their income that goes towards debt repayment and allows them to plan for repaying their debt sooner, which can consequently reduce their debt over time.
Meeting Lender Requirements
Lenders usually prefer a DTI ratio of 36% or lower for various types of loans.
Risk Management
For lenders, the DTI ratio is a risk management tool. It helps them assess the likelihood of loan repayment and reduce the risk of default.
How is the Debt to Income Ratio Calculated?
The Debt-to-Income (DTI) ratio is calculated by dividing an individual’s total monthly debt payments by their gross monthly income and multiplying the result by 100 to get a percentage.
Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how to calculate it:
Step 1: Determine Total Monthly Debt Payments
Include all your recurring monthly debt obligations, such as mortgage or rent payments, car loan payments, student loan payments, credit card payments (usually the minimum payment due), personal loan payments, and any other debt payments.
Step 2: Calculate Gross Monthly Income
Gross monthly income is the total income earned before taxes and deductions. This includes salary or wages, bonuses and commissions, overtime pay (if regular), pension, and any other sources of regular income.
Step 3: Apply the Formula
Use the following formula to calculate the DTI ratio:
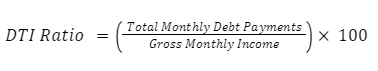
Let’s understand the DTI calculation with an example:
Step 1: Determine Total Monthly Debt Payments
- Home Loan EMI: ₹30,000
- Car Loan EMI: ₹8,000
- Education Loan EMI: ₹4,000
- Credit Card Minimum Payment: ₹3,000
Total Monthly Debt Payments = ₹30,000 + ₹8,000 + ₹4,000 + ₹3,000 = ₹45,000
Step 2: Calculate Gross Monthly Income
- Salary: ₹1,20,000
- Bonus: ₹10,000
Gross Monthly Income = ₹1,20,000 + ₹10,000 = ₹1,30,000
Step 3: Calculate DTI Ratio
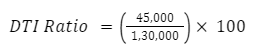
DTI Ratio ≈ 34.62 %
This percentage indicates that 34.62% of the individual’s gross monthly income is used to cover debt payments, which can help lenders assess their creditworthiness.
What is a Good Debt to Income Ratio?
A good Debt-to-Income (DTI) ratio suggests a manageable level of debt relative to income, indicating financial stability and the ability to handle additional borrowing when necessary.
Here are some general guidelines for what constitutes a good DTI ratio:
Lenders usually prefer a DTI ratio of 36% or lower. You will likely be seen as a low-risk borrower who responsibly manages debt.
While not ideal, many lenders will still consider borrowers with a DTI ratio in this range, especially if other factors (such as a high credit score) are favorable.
Borrowers may still qualify for loans, but the interest rates and terms might not be as favorable as those offered to individuals with lower DTI ratios.
A DTI ratio above 43% is generally considered high and may indicate that the borrower has too much debt. This can make it challenging to secure loans, and if approved, the terms may include higher interest rates.
Borrowers with high DTI ratios may have difficulty managing monthly payments and are at greater risk of defaulting on their loans.
Conclusion
The debt to income ratio is an important metric that plays a significant role in lenders’ creditworthiness assessments and can help individuals determine their financial stability as well. A lower DTI ratio indicates a better balance between debt and income, increasing the likelihood of loan approval and favorable terms.
The DTI ratio is a significant factor when it comes to approvals and deciding terms for personal loans. Lenders use this figure to determine your ability to repay the loan while managing existing obligations. A lower DTI ratio enhances your chances of securing a personal loan with better interest rates and terms.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does the DTI ratio affect loan approval?
A lower DTI ratio increases the likelihood of loan approval and can result in better interest rates and loan terms. Lenders use the DTI ratio to assess the risk of lending to a borrower; a higher ratio suggests greater risk.
Can I improve my DTI ratio?
Yes, you can improve your DTI ratio by increasing your income or reducing your debt. Strategies include paying off high-interest debts, avoiding new debt, and refinancing existing loans to lower monthly payments.
Does the DTI ratio affect all types of loans?
Yes, the DTI ratio is an important factor for various types of loans, including mortgages, car loans, and personal loans. Each type of loan may have different acceptable DTI ratio thresholds, but a lower ratio is generally preferred across loan types.
How often should I check my DTI ratio?
It’s a good idea to check your DTI ratio periodically, especially before applying for a loan. Regular monitoring can help you stay on top of your financial health and make informed decisions about managing debt.
What happens if my DTI ratio is too high?
If your DTI ratio is too high, you may have difficulty securing loans or may receive less favorable terms and higher interest rates. It indicates that you are over-leveraged and may struggle to manage additional debt. You can try to pay off existing debts to maintain your DTI ratio.